Setting Up VSCode for Linux
This page focuses on how to initially setup VSCode, specifically from the perspective of developing a module/plugin for NWChemEx on a Linux machine.
Adding Extensions
By default VSCode is pretty bare bones. Additional features are added/enabled by installing extensions. When you load up source code VSCode will inspect it and automatically recommend you install the corresponding extenstion (if it’s not installed already). For developing NWX we recommend you minimally install:
ms-vscode.cpptoolsms-vscode.cmake-toolsms-python.python
Fig. 10 Location of the extensions view.
To install an extension click on the extensions view (see Fig. 10) and search for the identifiers given in the above list.
Creating a Workspace
When you first start up VSCode you will have an empty workspace. We need to add content to that workspace.
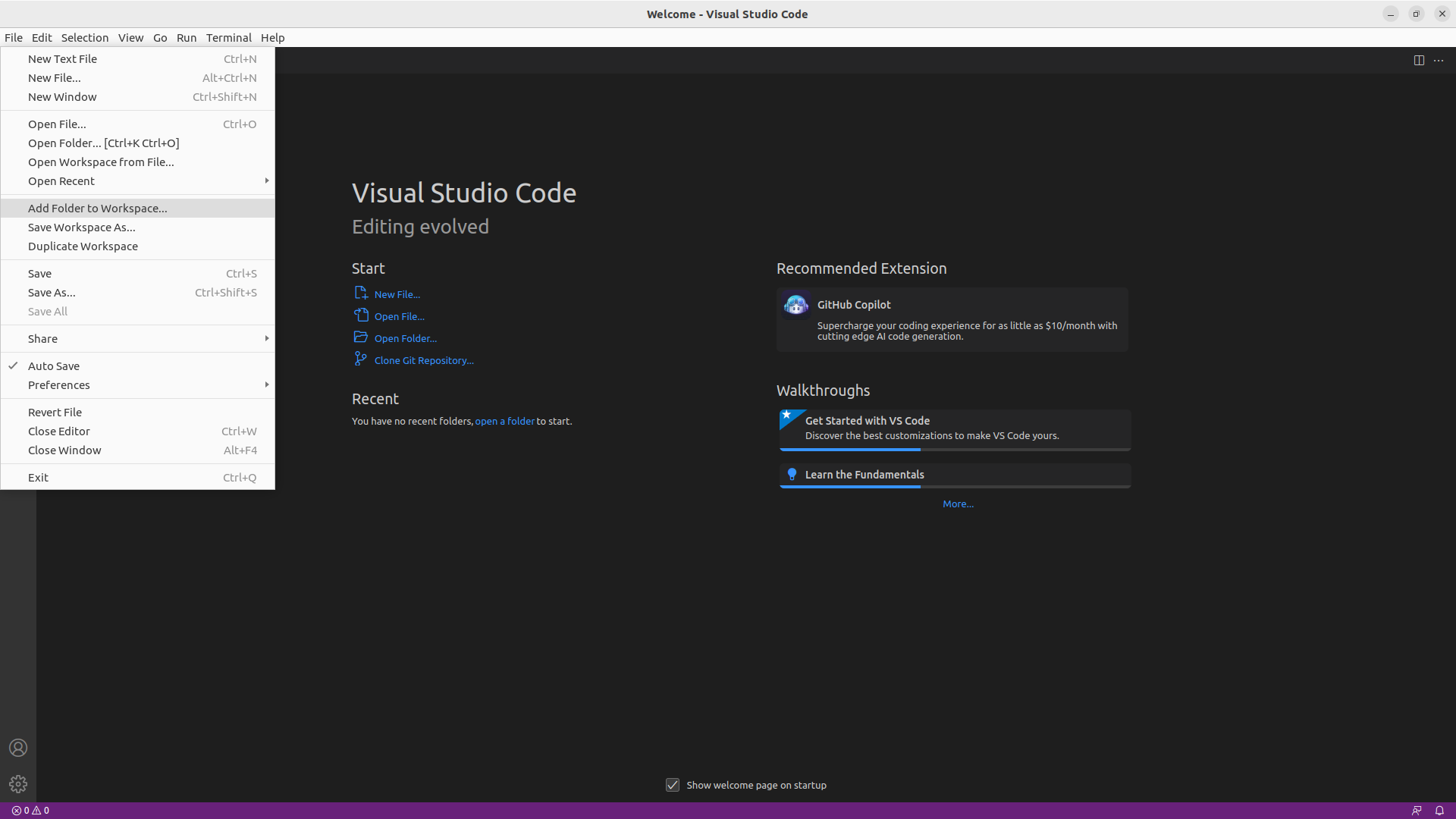
Fig. 11 Navigate to files->add folder to workspace.
To do this navigate to files->add folder to workspace as shown in
Fig. 11. This will bring up a file explorer,
which you should then use to navigate to the root directory of the repository
you want to add.
Fig. 12 The explorer icon.
To see the repositories you’ve added so far click on the explorer icon shown in Fig. 12.
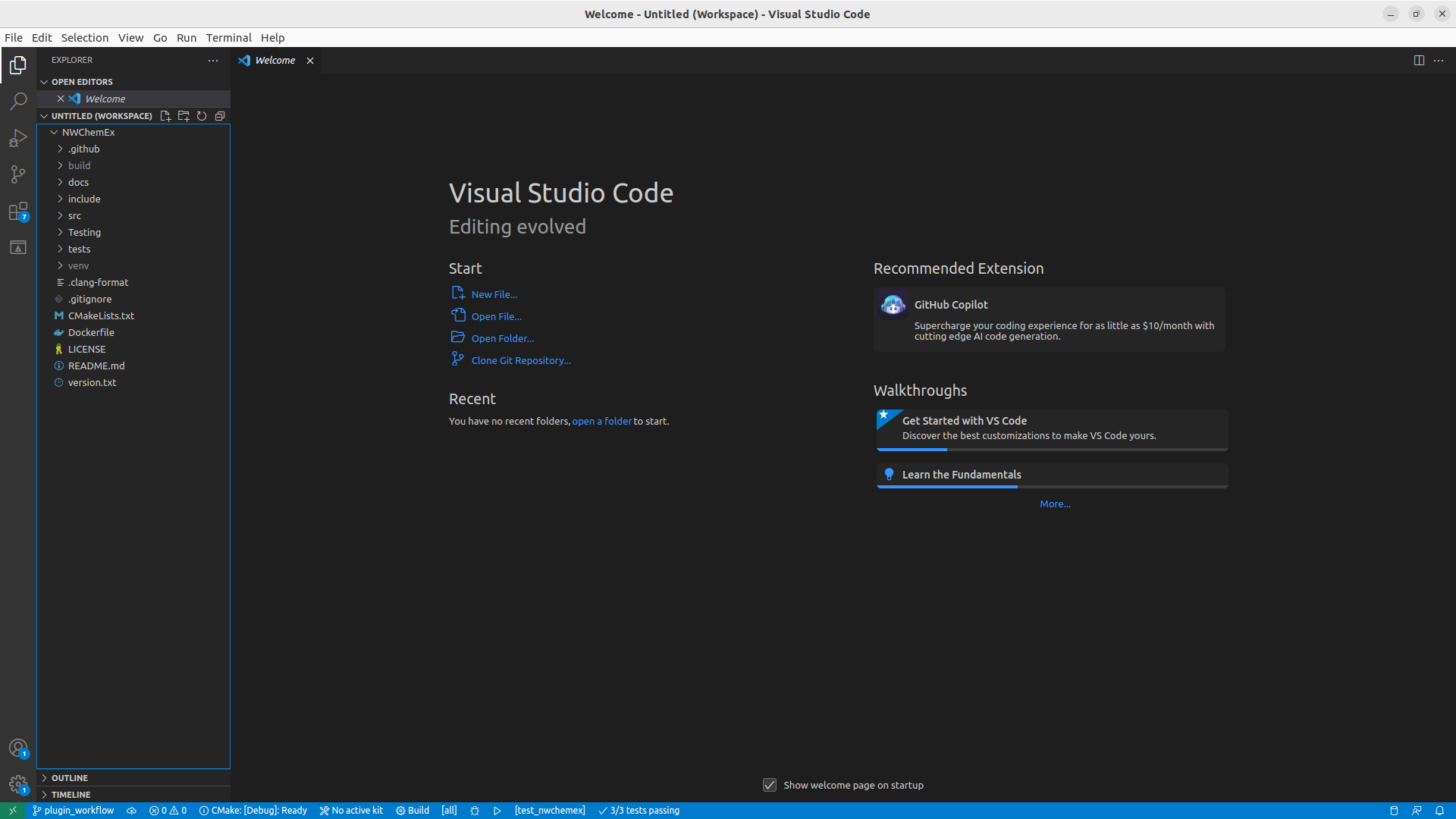
Fig. 13 View of VSCode with the explorer pane open.
This will open the explorer pane and VSCode will look something like shown in Fig. 13. For developing an NWChemEx module/plugin you will minimally want to have the repositories for NWChemEx and your plugin in your workspace. Repeat adding folders for each other repository you want to have in your workspace.
Note
AFAIK adding each repo individually in this manner is the only way for the CMake extension to properly register the root CMakeLists.txt for each repo.