How Does run_as work?
ModuleManager::run_as is the workhorse of running a call graph. The point
of this page is to succinctly summarize the behind-the-scenes actions of this
function.
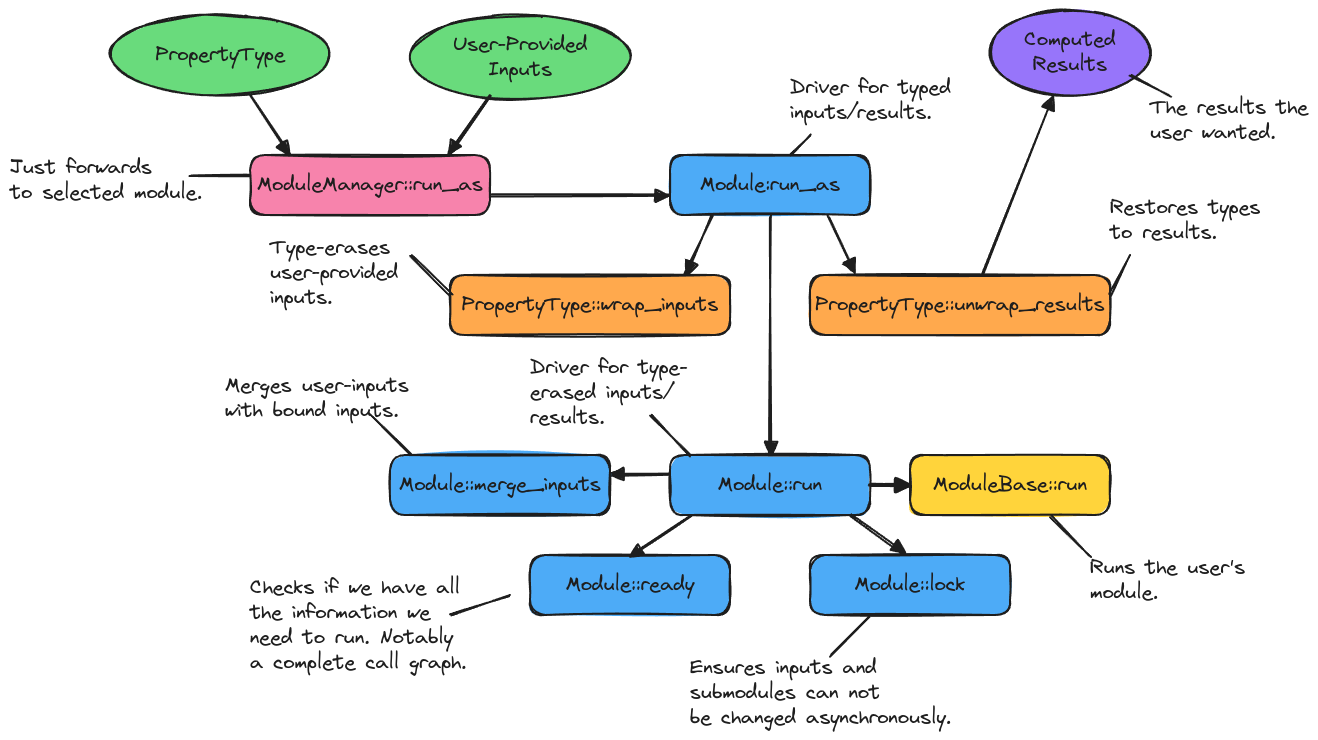
Fig. 15 Overview of the control flow of ModuleManager::run_as. Boxes denote
methods, ovals data. Arrows between methods point from caller to the callee.
Arrows stemming from data indicate data is input. Arrows ending in data
indicate that data results. When a method calls multiple sub-methods the
call order is depicted left-to-right. Note pre_run and post_run are
conceptual
The call graph of ModuleManager::run_as (as seen from C++) is summarized in
Fig. 15. Briefly:
Many users enter the call graph via
ModuleManager::run_as; however, this method simply wraps retrieving the specified module and forwarding the results to that module’sModule::run_asmethod.Module::run_asis the typed user interface. It works with the objects’ native C++ types, i.e., inputs and results are actual C++ objects. Under the hoodModule::run_asis responsible for type-erasing inputs and restoring types to results.PropertyType::wrap_inputsthis is the method thatModule::run_ascalls to type-erase the inputs. The property type class is essentially a schema written in terms of domain-specific types.With type-erased inputs the next call is to the type-erased user-interface,
Module::run.The first thing
Module::rundoes is to merge the user-provided inputs with the bound inputs. The result is the full set of inputs for the module.Next,
Module::rundetermines if the module is ready to run, e.g., does it have all the inputs needed to run? Has a submodule been assigned to each callback point? Is each submodule ready to run?Assuming the module is ready to run,
Module::runthen locks the module (and all submodules). A locked module can no longer have its options or submodules changed.After locking the module, the actual module contents are run via
ModuleBase::run(which calls the derived class’srun_method).The results of
Module::runare type-erased, so the final step is forModule::run_asto restore their types before returning them to the user.